Skincare treatments continue to evolve, offering effective ways to improve skin health without surgery or lengthy downtime. One treatment that continues to grow in popularity...
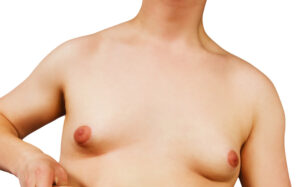
Gynecomastia refers to the enlargement of breast tissue in males. It is a benign (non-cancerous) condition caused by an increase in glandular breast tissue. In some cases, an increase in chest size may be due to excess fat rather than glandular tissue — a condition commonly referred to as pseudogynecomastia.
Gynecomastia can affect males at any stage of life, but it most commonly occurs during infancy, puberty, and later adulthood. It is very common, with more than half of males experiencing it at some point. The condition is most often linked to hormonal imbalance, particularly changes in testosterone and oestrogen levels.
While gynecomastia does not pose a physical health risk, it can have a significant impact on confidence and self-esteem. Emotional wellbeing is just as important as physical health, and anyone experiencing distress or concern related to gynecomastia is encouraged to seek professional advice.
Signs and Sensations of Gynecomastia
Gynecomastia often presents as a small, firm, button-like lump beneath the nipple. This may be visible or felt when pressing on the area and can sometimes feel tender or sensitive. The tissue may move slightly within the breast, and enlargement can affect one or both sides of the chest.
In contrast, chest enlargement caused by excess body fat — known as pseudogynecomastia — tends to appear as a more general increase in chest size rather than a defined lump.
Although gynecomastia is far more common, it’s important to be aware that male breast cancer can also cause breast lumps. While rare, any new or unusual changes in the chest should be assessed by a healthcare professional, who may recommend further examination or imaging to confirm the cause.
Possible Causes of Gynecomastia
Hormonal Imbalance
Gynecomastia occurs when there is an increase in glandular breast tissue, most commonly due to a hormonal imbalance between oestrogen and testosterone. Oestrogen promotes the growth of breast tissue, while testosterone counteracts this effect. When oestrogen levels rise or testosterone levels fall, breast tissue can enlarge.
This imbalance is most likely to occur during periods of natural hormonal change, including:
-
Infancy: Many male newborns experience temporary breast enlargement due to exposure to maternal hormones. This usually resolves within a few weeks.
-
Puberty: Breast enlargement is common during adolescence, often caused by a temporary rise in oestrogen relative to testosterone. In most cases, this settles within six months to two years.
-
Later adulthood: Gynecomastia becomes more common with age as testosterone levels naturally decline and medication use becomes more frequent.
These forms of gynecomastia are generally harmless, though they can still affect confidence and wellbeing.
Underlying Medical Conditions
In some cases, gynecomastia may be linked to an underlying health condition. These conditions often present with additional symptoms and may require medical evaluation and treatment. Examples include:
-
Hormonal or endocrine disorders
-
Liver or kidney disease
-
Genetic conditions affecting hormone production
-
Tumours affecting hormone-regulating glands or the testes
Medications and Substances
Certain medications can contribute to the development of gynecomastia by affecting hormone levels or how the body processes them. Recreational substances and the misuse of anabolic steroids may also increase the risk.
If gynecomastia develops suddenly, worsens, or is accompanied by other symptoms, it’s important to seek professional medical advice to determine the underlying cause and appropriate next steps.
Can Gynecomastia Resolve on Its Own?
In many cases, gynecomastia is temporary. In newborns and adolescents, it often disappears naturally once hormone levels stabilise. However, when gynecomastia is linked to long-term hormonal imbalances, such as consistently low testosterone levels, it may persist without medical treatment.
Living with gynecomastia can feel frustrating, particularly if it affects confidence or self-image. If the condition has been present for a long time or is causing emotional distress, it’s important to speak with a healthcare professional for advice and reassurance.
Can Exercise Reduce Gynecomastia?
If chest enlargement is caused by excess body fat (pseudogynecomastia), weight loss through diet and exercise may help reduce its appearance.
However, true gynecomastia caused by hormonal imbalance is unlikely to improve with exercise alone. While physical activity has many health benefits, it cannot reverse the growth of glandular breast tissue driven by hormone levels.
Managing and Treating Gynecomastia
Not everyone with gynecomastia requires treatment, particularly if the condition is mild or temporary. However, if treatment is desired or medically necessary, options will depend on the underlying cause and individual circumstances.
Medication review
If gynecomastia is linked to a medication or substance, a healthcare professional may recommend adjusting the dosage, switching medications, or stopping use altogether. It’s important to discuss all prescription, over-the-counter, and supplement use with a provider and never stop prescribed medication without medical advice.
Treating underlying conditions
When gynecomastia is caused by an underlying medical issue, such as a hormonal disorder, addressing that condition may also reduce breast tissue enlargement.
Surgical treatment
Some individuals choose surgical treatment, commonly referred to as male breast reduction surgery, to remove excess glandular tissue and improve chest contour. This is typically an elective procedure and may be considered when gynecomastia persists or significantly affects confidence and quality of life.
Take the first step towards a flatter, more confident chest.
Book a consultation with Dr Fasano to discuss personalised gynaecomastia surgery options and discover how precise removal of glandular tissue and fat can help you achieve lasting, natural-looking results.