Understanding VASER Lipo VASER liposuction is an advanced body contouring procedure designed to remove stubborn fat deposits while enhancing the body’s natural shape. It is...
Gynecomastia refers to the enlargement of male breast tissue, typically caused by an imbalance in hormones such as oestrogen and testosterone. In contrast, chest fat develops from an accumulation of fatty tissue in the chest area, often related to being overweight or leading a sedentary lifestyle.
Although both conditions can appear similar and are commonly referred to as “man boobs” or “moobs,” they differ in their underlying causes, symptoms, and treatment approaches.
If you’re experiencing excess fullness or tissue in the chest area, understanding the distinction between gynecomastia and chest fat is essential. Knowing the difference can help identify the root cause and guide you towards the most effective treatment options.
About Gynecomastia
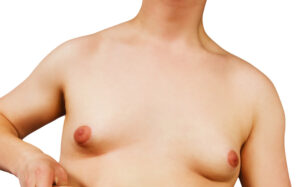
Gynecomastia, commonly referred to as male breast enlargement, occurs when there is an abnormal increase in breast tissue in men. This involves the growth of glandular (ductal) tissue, connective tissue, and fat, which can create the appearance of more prominent, female-like breasts. The word “gynecomastia” comes from the Greek words gyne (meaning woman) and mastos (meaning breast).
While gynecomastia is a physical condition, its effects are often emotional too. Many men report feeling self-conscious about their appearance, avoiding situations where they might be shirtless—such as at the beach or gym—or choosing loose clothing to conceal their chest. In some cases, the condition can also cause tenderness or discomfort.
The good news is that gynecomastia is a common and usually benign condition. It affects around half of all men at some point in their lives and often occurs during times of hormonal change, such as infancy, puberty, and older age. For teenage boys, temporary breast enlargement is particularly common and typically resolves on its own within a few months to two years.
The primary cause of gynecomastia is a hormonal imbalance between oestrogen and testosterone. Oestrogen stimulates breast tissue growth, while testosterone counteracts this effect. When the balance shifts and oestrogen activity becomes relatively higher, breast tissue can enlarge.
The reason for this imbalance is not always clear, but several factors may contribute, including:
- Hormonal conditions such as hypogonadism or thyroid disorders
- Liver or kidney disease, including cirrhosis and renal failure
- Obesity, which can increase oestrogen production in fat tissue
- Malnutrition or recovery from significant weight loss
- Certain medications or recreational drugs that alter hormone levels
- In rare cases, tumours affecting the testes, adrenal glands, or pituitary gland
Although gynecomastia can sometimes be uncomfortable or distressing, effective treatments are available—ranging from medical evaluation and lifestyle changes to surgical correction, depending on the underlying cause.
Gynecomastia vs Chest Fat: Knowing the Difference
Although gynecomastia and chest fat can look similar, they are two very different conditions.
Gynecomastia occurs when there is an overgrowth of glandular and connective tissue in the male chest, usually caused by a hormonal imbalance between oestrogen and testosterone. In contrast, chest fat is simply the accumulation of fatty tissue in the chest area, often related to overall weight gain or lack of physical activity.
While chest fat can often be reduced through diet and exercise, true gynecomastia does not go away on its own once established and may require surgical treatment to remove the enlarged glandular tissue.
Below are some key differences to help tell them apart:
Gynecomastia
-
Feels firm, rubbery, or dense to the touch
-
Usually begins as a disc-like lump beneath the nipple
-
Gives the chest a rounded, breast-like appearance
-
May cause tenderness or discomfort
-
Does not respond to diet or exercise
-
In some cases, the nipple and areola may protrude more prominently
Chest Fat
-
Feels soft and pliable, similar to other body fat
-
Linked to weight gain or higher body fat percentage
-
Often lacks a defined shape and may sag slightly
-
Painless and not tender to touch
-
Can improve with regular exercise, healthy diet, and weight loss
How Does Gynecomastia Surgery Work?
Gynecomastia surgery is designed to create a flatter, firmer, and more masculine-looking chest by removing excess tissue. The procedure is customised to each patient, depending on the type and amount of tissue that needs to be treated.
In many cases, liposuction is used to remove unwanted fat through small, discreet incisions, leaving minimal scarring. When glandular breast tissue or excess skin is also present, a technique called excision may be performed to carefully remove these tissues and refine the chest contour. For patients requiring more extensive reshaping, both methods can be combined for the best possible results.
The surgery is performed under local or general anaesthesia and typically takes around 1 to 2 hours. It is carried out as an outpatient procedure, meaning patients can go home the same day.
Recovery is generally straightforward—most people are able to return to normal daily activities within 3 to 7 days, depending on the extent of their procedure and individual healing rates.
Considering Gynecomastia Surgery?
If you’re struggling with excess chest tissue and want to achieve a flatter, more defined chest, book a consultation with Dr Leonardo Fasano. With extensive experience in male chest contouring and gynecomastia surgery, Dr Fasano provides individualised treatment plans and advanced surgical techniques to deliver natural, confident results.
Contact Dr Leonardo Fasano today to arrange a consultation and take the first step towards restoring your confidence and achieving a more sculpted chest.